近年來�,雙特異性治療性抗體已成為腫瘤、炎癥和傳染病治療的一個有前途的研究領(lǐng)域����。它們的雙靶點識別能力允許對新的治療假設(shè)進行測試����,傳統(tǒng)的單特異性抗體將缺乏所需的靶點參與模式。在極其多樣的雙特異性抗體結(jié)構(gòu)中�����,旋鈕進入孔(KIH)技術(shù)得到了廣泛應(yīng)用���,該技術(shù)涉及工程CH3結(jié)構(gòu)域�����,在每個重鏈中創(chuàng)建一個“旋鈕”或一個“孔”�,以促進異源二聚����。Knob-into-Hole (KiH)旋鈕插入孔技術(shù)利用抗體Fc片段CH3區(qū)域的互補突變實現(xiàn)重鏈異源二聚。
?
Adipogen利用KIH (Knobs-into-Holes) 技術(shù)開發(fā)了一系列的可以增強細胞活性和穩(wěn)定性的單體細胞因子:?
白細胞介素-2(IL-2)是一種133個氨基酸的糖蛋白,具有一個分子內(nèi)二硫鍵和可變糖基化����。由活化T細胞分泌,誘導(dǎo)活化T細胞�����、自然殺傷細胞和淋巴因子活化殺傷細胞的增殖和成熟��。IL-2還刺激產(chǎn)生抗體的B細胞增殖���,激活中性粒細胞��,并誘導(dǎo)單核細胞分泌IFN-γ�����、TNF-α和-β����。此外�����,研究表明,IL-2是激活誘導(dǎo)凋亡所必需的��,這是免疫系統(tǒng)中一種重要的穩(wěn)態(tài)機制����,參與維持外周對自身抗原的耐受性。
IL-2促進T細胞增殖����,尤其是原始T細胞��?���;罨疶細胞上的IL-2信號通過由IL-2、IL-2Rα(CD25)�、IL-2Rβ和IL-2Rγ組成的四級高親和力受體復(fù)合物影響。原始T細胞對IL-2相對不敏感����,因為它們只表達少量的IL-2Rβ和IL-2Rγ。它們僅在CD25表達后獲得敏感性�,CD25捕獲細胞因子并將其呈現(xiàn)給IL-2Rβ和IL-2Rγ受體。
?
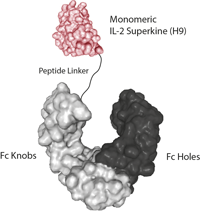
IL-2超因子(Fc)是IL-2的一種人工變體�,稱為H9���,在L80F/R81D/L85V/I 86V/I92F位置含有突變。這些突變位于該分子的核心����,其作用是穩(wěn)定該結(jié)構(gòu),并使其形成受體結(jié)合構(gòu)象��,模擬與CD25結(jié)合的天然IL-2�。這些突變有效地消除了IL-2對CD25表達的功能需求,并誘導(dǎo)T細胞增殖����。與白細胞介素-2相比,白細胞介素-2超因子可誘導(dǎo)細胞毒性T細胞的優(yōu)越擴增��,從而改善體內(nèi)抗腫瘤反應(yīng)����,并通過降低T調(diào)節(jié)細胞的擴增和減少肺水腫,相應(yīng)地降低毒性��。
?
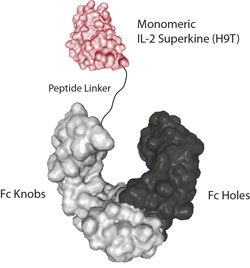
IL-2超因子(Fc)另外一個變體����,稱為HT9�����,可以降低了IL-2Rγ的結(jié)合�����,并促進了CD8+T細胞的擴增����,而無需驅(qū)動末端分化�。在黑色素瘤和急性淋巴細胞白血病小鼠模型中,經(jīng)H9T擴增的TCR轉(zhuǎn)基因和嵌合抗原受體修飾的CD8+T細胞在體內(nèi)表現(xiàn)出更強的抗腫瘤活性��。被稱為H9T的IL-2新變體有助于將活化的CD8+T細胞維持在干細胞樣狀態(tài)���,在兩種小鼠模型中具有更強的抗腫瘤活性。與IL-2超因子(H9)一樣�����,IL-2超因子(H9T)也作用于人類T細胞�。
? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ?
產(chǎn)品信息:
Human IL-2 Superkine H9T (monomeric):Fc-KIH
?
貨號:AG-40B-0223
名稱:IL-2 Superkine H9T (monomeric):Fc-KIH (human) (rec.)
規(guī)格:10 μg、3 x 10 μg�、100 μg
反應(yīng)種屬:Human、Mouse
?
蛋白表達體系:HEK 293 cells
蛋白序列:The extracellular domain of human IL-2 (aa 21-153) (mutant H9T containing the mutations of H9: L80F / R81D / L85V / I 86V / I92F and the new mutation Q126T) is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (Knobs-into-Holes technology).
特異性:Binds to human and mouse IL-2R.
分子量大?��。?/span>~45kDa and 28kDa (SDS-PAGE)
純度:≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
內(nèi)毒素含量:<0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test).
陰性對照蛋白:Fc-KIH (human) IgG1 Control (rec.)
提供形式:固體
保存條件:4度保存����,長期保存需放-20度���。避免反復(fù)凍融����。
?
參考文獻:
An engineered IL-2 partial agonist promotes CD8+ T cell stemness: F. Mo, et al.; Nature?597,?544 (2021)
?
訂購詳情:
貨號 | AG-40B-0223 | AG-40B-0222 | AG-40B-0224 | AG-40B-0225 |
產(chǎn)品名稱 | IL-2 Superkine H9T (monomeric):Fc-KIH (human) (rec.) | IL-2 Superkine (monomeric):Fc-KIH (human) (rec.) | IL-2 (human) (monomeric):Fc-KIH (human) (rec.) | IL-2 (mouse) (monomeric):Fc-KIH (human) (rec.) |
規(guī)格 | 10 μg�����、3 x 10 μg�、100 μg | 10 μg、3 x 10 μg��、100 μg | 10 μg、3 x 10 μg���、100 μg | 10 μg���、3 x 10 μg、100 μg |
反應(yīng)種屬 | Human����、Mouse | Human、Mouse | Human���、Mouse | Human���、Mouse |
序列 | The extracellular domain of human IL-2 (aa 21-153) (mutant H9T containing the mutations of H9: L80F / R81D / L85V / I 86V / I92F and the new mutation Q126T) is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (Knobs-into-Holes technology) | Human IL-2 (aa 21-153) (mutant H9 containing the mutations L80F / R81D / L85V / I 86V / I92F) ?is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (Knobs-into-Holes technology) | Human IL-2 (aa 21-153) ?is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (Knobs-into-Holes technology) | Mouse IL-2 (aa 21-169) is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (Knobs-into-Holes technology) |
特異性 | Binds to human and mouse IL-2R. | Binds to human and mouse IL-2R (without CD25 requirement). | - | - |
陰性對照蛋白 | Fc-KIH (human) IgG1 Control (rec.)(AG-35B-0015) | Fc-KIH (human) IgG1 Control (rec.)(AG-35B-0015) | Fc-KIH (human) IgG1 Control (rec.)(AG-35B-0015) | Fc-KIH (human) IgG1 Control (rec.)(AG-35B-0015) |
應(yīng)用 | Triggers greater antitumor responses by maintaining stem-cell memory phenotype of CD8+ T cells. | Triggers far greater antitumor responses than native IL-2?in vivo?but with lower toxicity | - | - |
詳情請咨詢Adipogen全國授權(quán)一級代理-欣博盛生物科技?
全國服務(wù)熱線: 4006-800-892 ? ? ??郵箱: market@neobioscience.com?
深圳: 0755-26755892 ? ? ? ??北京: 010-88594029 ? ? ? ??上海: 021-34613729???????????
廣州:020-87615159?????????? 香港: 852-69410778?
代理品牌網(wǎng)站: m.smblzp.com?
自主品牌網(wǎng)站: www.neobioscience.net